Basic Introduction or Principle: We all are aware with the term "Generator". A device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy is known as generator. This generator makes rotate with the help of some kind of external energy. When this energy extract from the energy of steam, the plant is known as steam power plant. A simple steam plant works on Rankine cycle. In the first step, water is feed into a boiler at a very high pressure by BFP (boiler feed pump). This high pressurized water is heated into a boiler which converts it into high pressurized super heated steam. This high energized steam passes through steam turbine (a mechanical device which converts flow energy of fluid into mechanical energy) and rotate it. Owing to extract full energy of steam, three stage turbines is used which is known as LPT (Low pressure turbine), IPT (intermediate pressure turbine) and HPT (High pressure turbine). The turbine shaft is connected to the...
In the present time four stroke engines is very popular in automobile industries. Today we will learn about how four stroke petrol and diesel engine works. In most of car, buses, bikes, and scooters, we are using four stroke engines because of its higher millage and sufficient power (torque). A four stroke engine means that the piston passes two times from top dead center to bottom dead center and crankshaft revolves two complete revolutions in one power stroke (one time of fuel burns).
In present time two types of four stroke engines used in automobile. These are
1. Spark ignition engine (petrol engine)
2. Compression ignition engine (diesel engine)
How Does Four Stroke Petrol Engine Work?
Four stroke spark ignition engine widely used in bikes, sport cars because of its higher speed. In this type of engine combustion of fuel ignite by the spark generate by an external spark plug. So it is known as spark ignition engine. This engine used petrol as the fuel because of its combustion temperature and other characteristics are suitable for this engine. So it is also known as the petrol engine.
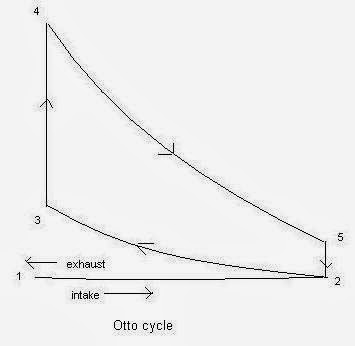
The four stroke engine works on Otto cycle. The power generation process in the four stroke spark ignition engine is divided into four thermal processes. Each process is run with one piston stroke. These processes are known as intake stroke, compression stroke, expansion stroke, exhaust stroke.
Intake stroke (suction stroke):
Air and fuel mixture enter into the cylinder during suction stroke. In the suction stroke piston moves from top dead center to bottom dead center and simultaneously inlet valve opens. At this time the pressure inside the cylinder is less than the atmospheric pressure so the air fuel mixture is sucked in the engine cylinder through the inlet port. The inlet valve remains open and exhaust valve remains close during this stroke. In this stroke the volume of cylinder increases and the pressure remain unchanged. This operation is represented by the line 1-2 in Otto cycle.
In this stroke the piston moves from bottom dead center to top dead center and compressed the enclosed air fuel mixture which is drawn into the cylinder during intake stroke. It compressed the air fuel mixture into 1/8 time to its original volume. Both inlet and exhaust valve remain closed during this stroke. At the end of the compression stroke when the piston reaches at top dead center the spark plug generate a spark which ignites the air fuel mixture. In this stroke the cylinder pressure increases and the volume of cylinder decreases. This stroke is represented by the line 2-3 in the Otto cycle.
At the end of the compression stroke, a spark generated by the spark plug which ignite the air fuel mixture. When the mixture is ignited the chemical process take place and produce combustion gases like carbon-di-oxide. These gases increase the cylinder pressure and temperature. The pressure force generated by the combustion of the fuel, exerts a force or thrust on piston and throws it from top dead center to bottom dead center. Thus the work is obtained in this stroke so it is also known as power stroke. During combustion of gases the cylinder pressure is suddenly increases and the volume of cylinder remain constant. This process is represented by the line 3-4 in Otto cycle. After combustion of the fuel, high pressure is generated which expand the piston form top dead center to bottom dead center. In the expansion the cylinder pressure is decreases and the volume of cylinder increases. This operation is presented by the curve line 4-5 in Otto cycle.
Exhaust stroke:
This is the last stroke of the cycle. The gases generated by the combustion of fuel are useless after the complete expansion of the piston. So it should be thrown out from the cylinder. At the end of the expansion stroke the exhaust valve opens. This time the cylinder pressure is higher than the atmospheric pressure. So these gases are escape from the cylinder. During this oppression the cylinder volume decreases and there is negligible change in the pressure of the cylinder. This operation is represented by the line 5-1 in the Otto cycle.
At the end of the exhaust stoke again air fuel mixture is drawn into the cylinder and this process running until the engine is start.
How Does Four Stroke Diesel Engine Work?
Four stroke compression ignition engines are widely used in cars and heavy motor vehicle such as truck and buses because of its higher torque at the lower speed. In this type of engine combustion of the fuel ignite by the temperature increase during compression. So it is known as compression ignition engine. This engine used diesel as the fuel so it is sometime called diesel engine.
The working of the compression ignition engine is slightly different of the spark ignition engine because of it works on Diesel cycle instead of Otto cycle.
The power generation process in the four stroke compression ignition engine is also divided into four thermal processes. Each process is run with one piston stroke. These processes are known as intake stroke, compression stroke, expansion stroke, exhaust stroke.
Intake stroke:
In the intake stroke of compression ignition engine only air is drawn inside the cylinder. In this stroke piston moves from top dead center to bottom dead center and simultaneously inlet valve opens. At this time the pressure inside the cylinder is less than the atmospheric pressure so the air is sucked in the engine cylinder through the inlet port. Sometimes the air is drawn by use of a pump to increase engine efficiency. The inlet valve remains open and exhaust valve remains close during this stroke. In this stroke the volume of cylinder increases and the pressure remain unchanged. This operation is represented by the line 1-2 in Diesel cycle.

Compression stroke:
In this stroke the piston moves from bottom dead center to top dead center and compressed the enclosed air which is drawn into the cylinder during intake stroke. It compressed the air into 1/22 time to its original volume. Both inlet and exhaust valve remain closed during this stroke. At the end of the compression stroke when the piston reaches at top dead center, fuel is injected into the cylinder by the injector. In this stroke the cylinder temperature and pressure of cylinder reaches very high. This stroke is represented by the line 2-3 in the Diesel cycle.
At the end of the compression stroke, fuel is injected into the cylinder by the injector in the form of fine spray. The compressed air temperature is sufficient high to ignite the fuel. When the mixture is ignited the chemical process take place and produce combustion gases like carbon-di-oxide. These gases increase the cylinder pressure and temperature. This pressure force generated by the combustion of the fuel, exerts a force or thrust on piston and throws it from top dead center to bottom dead center. Thus the work is obtained in this stroke so it is also known as power stroke. In diesel a metered quantity of fuel is injected into the hot compressed air in fine sprays by the injector and it starts burning at constant pressure. This process is represented by the line 3-4 in Diesel cycle. After combustion of the fuel, high pressure is generated which expand the piston form top dead center to bottom dead center. In the expansion the cylinder pressure is decreases and the volume of cylinder increases. This operation is presented by the curve line 4-5 in Diesel cycle.

Exhaust stroke:
This is the last stroke of the cycle. The gases generated by the combustion of fuel are useless after the complete expansion of the piston. So it should be thrown out from the cylinder. At the end of the expansion stroke the exhaust valve open. This time the cylinder pressure is higher than the atmospheric pressure. So these gases are escape from the cylinder. During this operation the cylinder volume decreases and there is negligible change in the pressure of the cylinder. This operation is represented by the line 5-1 in the Diesel cycle.
At the end of the exhaust stoke again air is drawn into the cylinder and this process running until the engine is start.







Very nice work sir
ReplyDelete